Health
Widely Used Methods for Treating Anemia
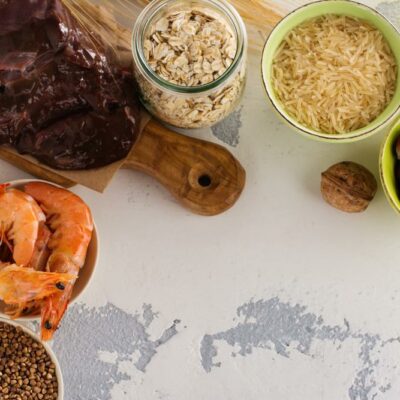
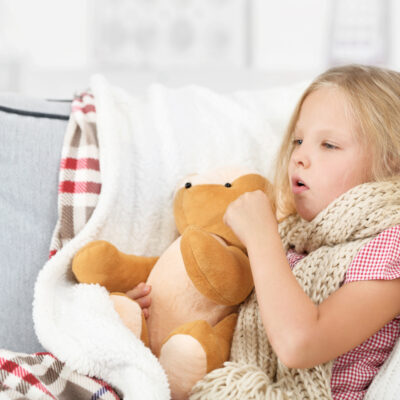
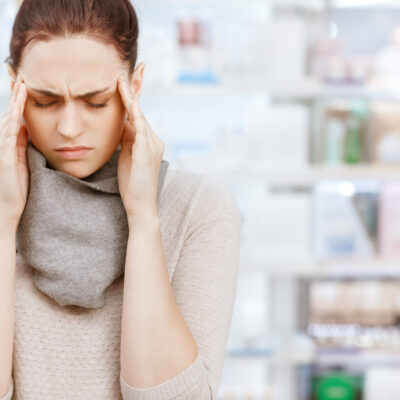
The most common blood disorder in the world, anemia is a condition in which a person has a deficiency in red blood cells, or hemoglobin. Because red blood cells are oxygenated, a decreased amount results in less oxygen to organs, often causing weariness, increased fatigue, accelerated heart rate, yellow skin, breathlessness, lightheadedness, chest pain, headache, and cold hands and feet. The leading cause for anemia is iron deficiency. Without sufficient iron levels, the body cannot produce the hemoglobin needed to produce red blood cells. However, an iron deficiency is not the only type of anemia. There are over 400 types of anemia, among the other main types are: Vitamin deficiency anemia due to low B12 for healthy red blood cell production. Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune disease due to lack of the intrinsic factor that helps the body absorb vitamin B12 in the intestine. Aplastic anemia, a life-threatening anemia that occurs when the body doesn’t produce adequate red blood cells. Hemolytic anemias, where red blood cells are destroyed faster than bone marrow can replace them. Sickle cell anemia, an inherited condition caused by a defective hemoglobin that makes abnormal crescent (sickle) shaped red blood cells that die prematurely. Bone marrow anemias, such as leukemia or myelofibrosis.
Read More